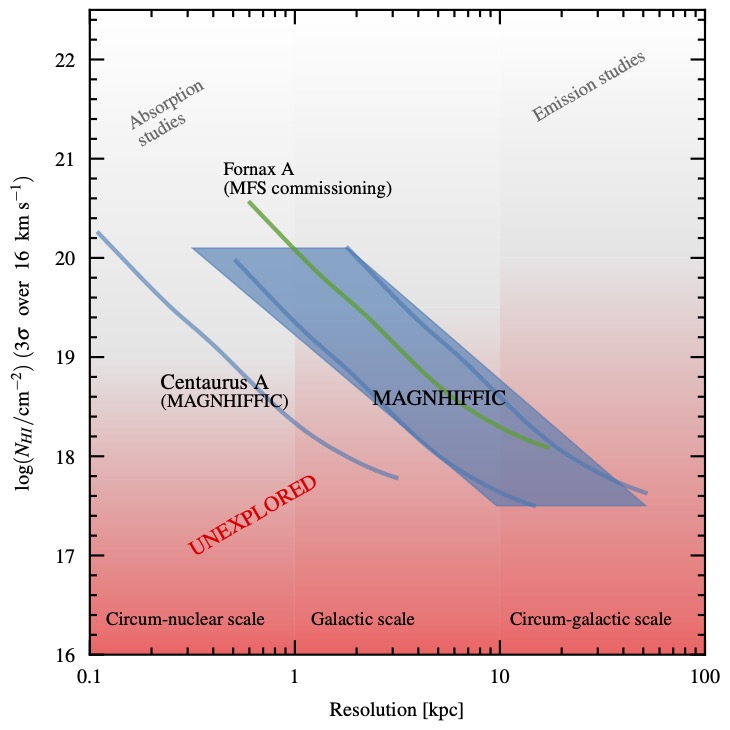
MAGNHIFFIC
will probe a part of parameter space in AGN studies that has not yet been observed with any radio telescope
, enabling us to study the typical column densities of neutral hydrogen (HI) inflows and outflows (10
18-19
cm-2
) with kilo-parsec resolution, or better. The
MeerKAT
observations will provide at least 10 times deeper HI column density sensitivity, while improving the spatial and spectral resolution by at least a factor 3. MAGNHIFFIC will be the benchmark study of the distribution and kinematics of the HI in galaxies hosting an AGN.
MAGNHIFFIC is a ground-breaking project that for the first time will study the process of feeding and feedback in 22 nearby AGN with different energetic outputs, different ages, in different hosts and in different environments. The sample is divided between radiative AGN (10 sources), and radio jetted AGN (12 sources). Sources have been selected where sensitive observations of the molecular and ionised gas showed indications of on-going feeding and/or feedback (e.g. Maccagni et al. 2018, Ruffa et al. 2019a, Mingozzi et al. 2018, Venturi et al. 2020).
Combining the HI with the molecular and ionised gas observations, MAGNHIFFIC will infer the physical conditions, the total mass of the multi-phase outflows and investigate their impact on the SF of the host galaxies.
From the timescales of the interaction events and by quantifying the effects of turbulence on the multi-phase IGM and ISM, MAGNHIFFIC will identify the AGN accretion mechanisms and study how they sustain recurrent nuclear activity.